1st: NIC that directly connect to internet.
Other: NIC which will act just any other interface of router holding other network.(It will also act as default gateway)
Lets take an example, see fig below,
In the figure as you can see there are 3 NIC one of which connects directly to Internet other two are used as router interface to create different networks.Lets start,
First we have to enable IP forwarding, to do that
Go to Run> type regedit
then follow path
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\TcpipParameters
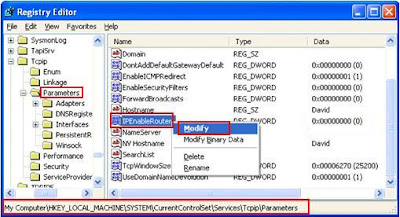
Right click IPEnableRouter registry object, and click Modify
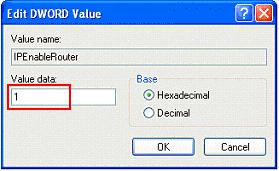
In the value data field enter 1. Its done click OK.
Now configure the network cards on the XP machine (router) with following info,
NIC-2
Network Card A (connect to network A):
IP: 10.10.10.1
Netmask: 255.255.255.0
Gateway (GW): [leave it blank]
NIC-3
Network Card B (connect to network B):
IP: 192.168.20.1
Netmask: 255.255.255.0
Gateway (GW): [leave it blank]
NIC-1
Network Card C (connect to Internet via cable/dsl connection)
This information will be based on the Internet connection service which you have subscribed.
Configure all the computers in network A with following information.
Network A
IP: 10.10.10.2-254
Netmask: 255.255.255.0
Gateway (GW): 10.10.10.1
Configure all the computers in network B with following information.
Network B
IP: 192.168.20.2-254
Netmask: 255.255.255.0
Gateway: 192.168.20.1
Other: NIC which will act just any other interface of router holding other network.(It will also act as default gateway)
Lets take an example, see fig below,
In the figure as you can see there are 3 NIC one of which connects directly to Internet other two are used as router interface to create different networks.Lets start,
First we have to enable IP forwarding, to do that
Go to Run> type regedit
then follow path
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\TcpipParameters

Right click IPEnableRouter registry object, and click Modify

In the value data field enter 1. Its done click OK.
Now configure the network cards on the XP machine (router) with following info,
NIC-2
Network Card A (connect to network A):
IP: 10.10.10.1
Netmask: 255.255.255.0
Gateway (GW): [leave it blank]
NIC-3
Network Card B (connect to network B):
IP: 192.168.20.1
Netmask: 255.255.255.0
Gateway (GW): [leave it blank]
NIC-1
Network Card C (connect to Internet via cable/dsl connection)
This information will be based on the Internet connection service which you have subscribed.
Configure all the computers in network A with following information.
Network A
IP: 10.10.10.2-254
Netmask: 255.255.255.0
Gateway (GW): 10.10.10.1
Configure all the computers in network B with following information.
Network B
IP: 192.168.20.2-254
Netmask: 255.255.255.0
Gateway: 192.168.20.1

